ABCN Busbar Arrangement in Distribution Cabinets: A Key Rule for Electrical Safety
ABCN Busbar Arrangement in Distribution Cabinets: A Core Principle of Electrical Safety
Inside every professionally built distribution cabinet, the neatly aligned **busbars—copper bars, conductor bars, or power distribution bars—**form the structural backbone of electrical energy transmission. These conductors carry high current and act as the critical link between transformers, switching devices, and downstream loads.
For electrical engineers, the arrangement of busbars is never arbitrary. It follows a strict and internationally recognized logic—the ABCN phase sequence rule, a key principle that ensures installation consistency and operational safety.
This article explains the ABCN arrangement requirements based on electrical installation practices and Chinese national standards.
1. Understanding ABCN: Functional Codes in Power Systems
In a three-phase system, each busbar corresponds to a specific electrical function:
A, B, C Phases (Live Conductors)
The three phase conductors of an AC system, spaced 120° apart in electrical phase angle. They form the core of industrial power distribution networks.
N Conductor (Neutral)
Provides the return path for unbalanced current and the reference potential for single-phase loads in three-phase four-wire systems.
PE (Protective Earth)
Although not part of ABCN, the PE conductor is essential for system protection. It is typically implemented using a yellow–green copper bar or grounding strip.
In engineering documentation and installation drawings, these conductors may all be classified under the busbar system but still require strict functional differentiation.
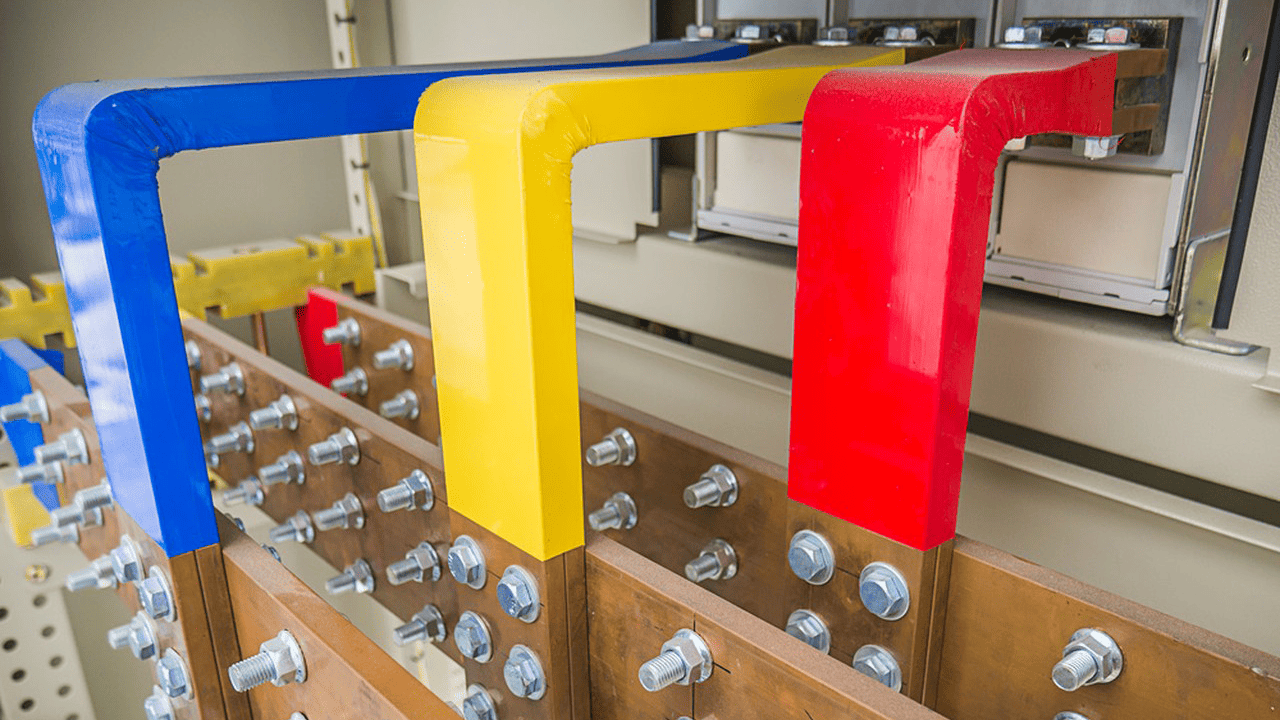
2. Standardized Busbar Arrangement: Requirements in Chinese National Standards
Chinese standards such as GB 7251 (LV switchgear) and GB 50054 (LV distribution design code) specify that busbars in a distribution cabinet must follow a clear and consistent phase sequence.
2.1 Horizontal Arrangement (Facing the Cabinet Front)
From front to back:
A — B — C — N
The A-phase busbar is closest to the operator, while the neutral conductor is positioned at the inner side.
2.2 Vertical Arrangement (Top-to-Bottom)
From top to bottom:
A — B — C — N
This configuration ensures consistency when connecting busway systems, upstream cabinets, and downstream equipment.
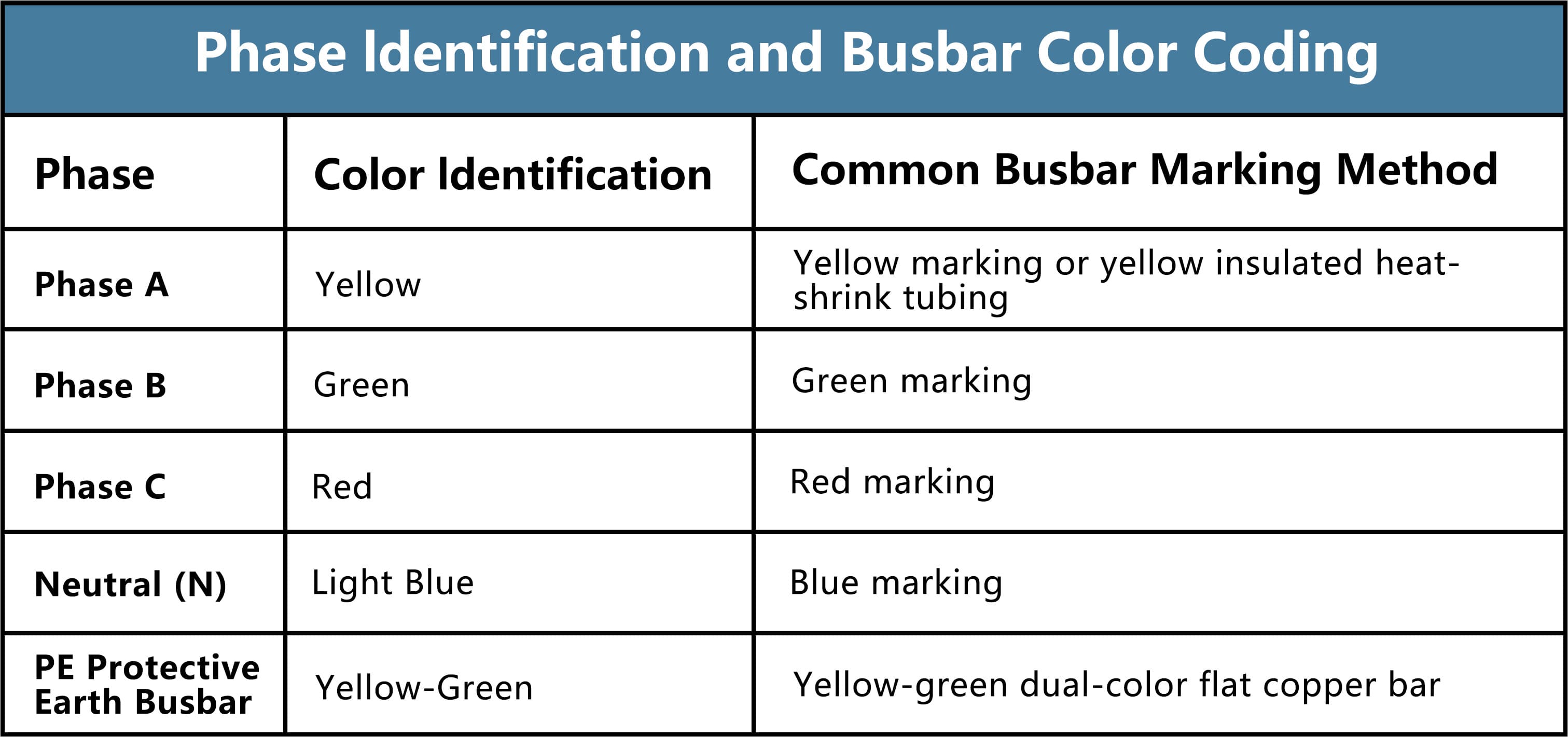
3. Color Identification: A Key Tool for Safe Recognition
According to GB/T 2681 – Color Identification for Conductors:
- A Phase: Yellow
- B Phase: Green
- C Phase: Red
- Neutral (N): Light Blue
- PE: Yellow–Green
These markings—applied by painting, insulation sleeves, or labels—allow engineers to quickly recognize conductor functions during installation, inspection, and maintenance.
4. Why the ABCN Sequence Matters
4.1 Ensures Installation and Maintenance Safety
A unified, predictable busbar sequence reduces the risk of misoperation during:
Voltage measurement
Isolation and switching
Grounding line connection
Fault repair under time pressure
It provides engineers with a stable and reliable working environment across different sites and manufacturers.
4.2 Guarantees Correct Operation of Downstream Equipment
Many three-phase devices—motors, VFDs, power capacitors—are sensitive to phase sequence.
A standardized ABC layout prevents:
Motor reverse rotation
VFD phase-failure alarms
Capacitor bank malfunction
Protection relay misoperation
4.3 Improves System Management and Fault Diagnosis
When schematics, wiring diagrams, and the physical busbar layout follow the same phase order, troubleshooting becomes significantly more efficient.
Engineers can quickly:
Trace conductor paths
Locate abnormal voltages
Perform power quality checks
4.4 Supports Standardized Manufacturing and Modular Design
For switchgear manufacturers, consistent phase sequencing enables:
Modular busbar design
Simplified production processes
Higher assembly consistency
Improved overall product quality
This is essential for modern, platform-based cabinet production.
5. Beyond ABCN: Engineering Precision in Busbar Systems
In addition to correct phase sequence, a high-quality busbar system must meet:
- Electrical clearance and creepage distance requirements
- Current-carrying capacity and temperature-rise limits
- Short-circuit thermal and dynamic withstand performance
- Reliable insulation design and arc-fault prevention
- High-precision bending, surface finishing, and anti-oxidation treatment
These elements jointly determine the long-term stability of a distribution cabinet.
Conclusion
The ABCN busbar arrangement is far more than a basic requirement—it is a fundamental engineering logic that runs through the entire lifecycle of electrical equipment: design, fabrication, installation, operation, and maintenance. Strict adherence to this sequence, combined with standardized color marking and high-quality busbar craftsmanship, forms the cornerstone of safe, reliable, and efficient power distribution.