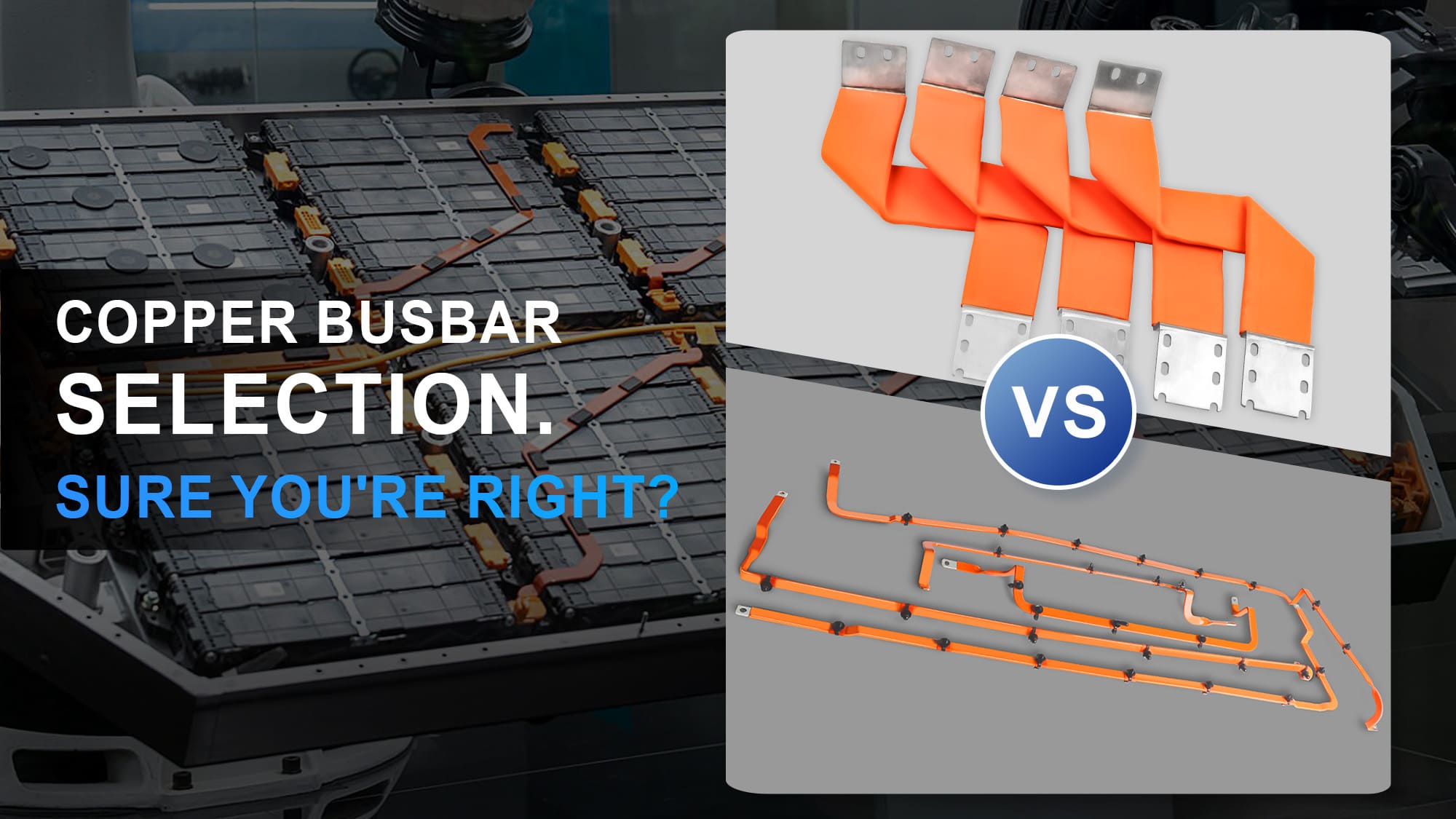
Rigid or Flexible? Copper Busbars for Efficient Thermal-Electrical Balance
Thermal control defines interconnection performance in high-efficiency energy systems. Rigid copper busbars enable directional heat conduction, while flexible laminated connectors provide heat dissipation and mechanical compliance. Backed by simulation-driven design and advanced manufacturing, RHI delivers low-temperature-rise, high-reliability interconnection solutions for next-generation new energy systems.
Thermal and Electrical Trade-Offs: Rigid vs. Flexible Copper Busbars
In electric drive systems and energy storage applications, current-carrying capability and thermal management performance directly define system efficiency limits, reliability, and service life. Rigid copper busbars and flexible copper laminated connectors are two fundamental conductor solutions. Their distinction goes far beyond a simple comparison of "conductivity" versus "flexibility" —the core difference lies in fundamentally different heat dissipation paths and thermal management philosophies. Understanding this distinction is essential for designing high-reliability, high-efficiency electrical interconnection systems.
1. Thermal Design: From Directed Conduction to Heat Spreading
Heat generation is an unavoidable byproduct of high-current transmission. Without effective thermal control, excessive heat leads to contact oxidation, increased resistance, insulation aging, and ultimately system failure.
1.1 Rigid Copper Busbars: High-Conductivity, Directional Heat Conductors
Primary heat path: Short, straight, and highly directional. Rigid copper busbars are typically manufactured from high-purity electrolytic copper through rolling, annealing, stamping, and precision bending processes. Their dense, monolithic structure results in extremely low thermal resistance.
Thermal logic: Active heat conduction. Heat—particularly localized hot spots at electrical joints—is rapidly conducted along the longitudinal axis of the busbar toward predefined thermal sinks such as liquid-cooled cold plates, enclosures, or external heat exchangers.
Optimal application scenarios: Rigid copper busbars are the preferred solution when a system features clearly defined active cooling paths. For example, in DC-link connections of motor inverters, rigid busbars efficiently transfer heat generated at high-current power module terminals directly to the cooling plate, delivering superior thermal performance and temperature stability.
1.2 Flexible Copper Laminated Connectors: Distributed Heat Spreading
Primary heat path: Distributed and non-linear. Constructed from multiple layers of ultra-thin copper foils (typically ~0.1 mm) laminated and metallurgically bonded, flexible connectors form a compliant current-carrying bundle.
Thermal logic: Passive heat dissipation. Their thermal performance relies on a large specific surface area created by the multi-foil structure, enabling effective heat rejection through natural convection and thermal radiation. In addition, their higher thermal mass provides buffering against transient temperature spikes.
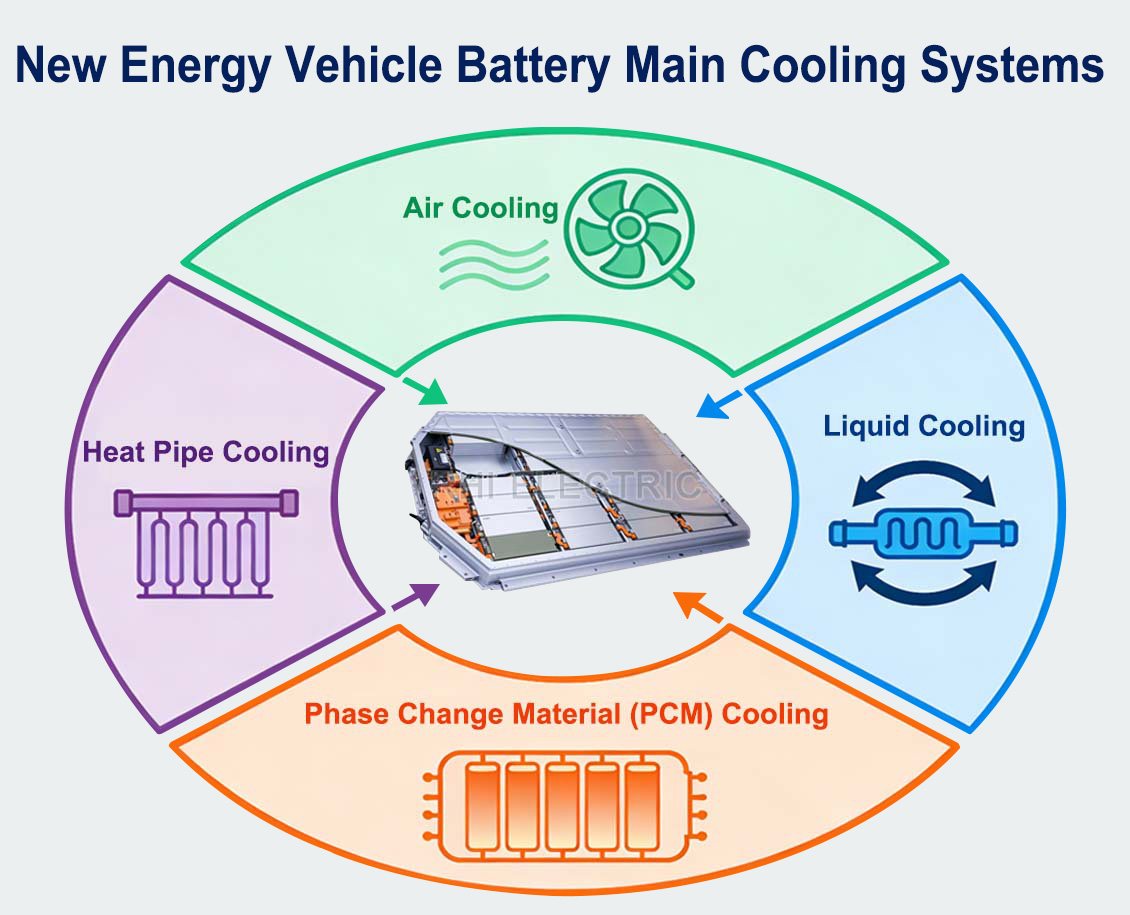
Optimal application scenarios: Flexible copper connectors excel in environments requiring vibration tolerance, dimensional compensation, and thermal buffering—especially where forced cooling is limited or unavailable. Within battery modules, for instance, interconnections between cell terminals must accommodate manufacturing tolerances, vibration, and thermal expansion. At the same time, the laminated foil structure enhances passive heat dissipation within confined or semi-sealed spaces.
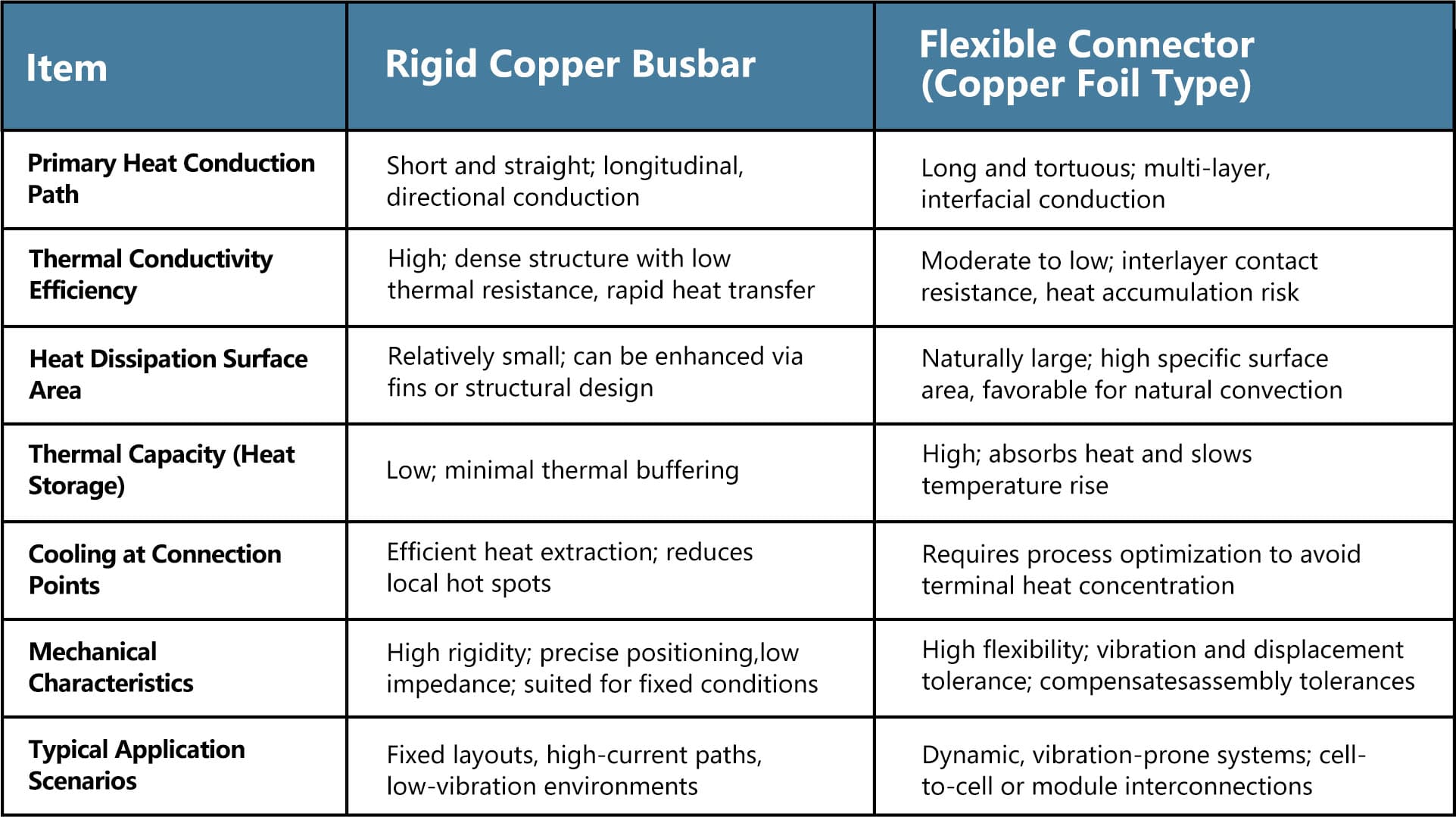
2. New Energy Applications: Optimizing Rigid and Flexible Busbars
In electric vehicles and energy storage systems, rigid copper busbars and flexible copper connectors serve clearly differentiated roles. Selection is driven by a comprehensive evaluation of electrical performance, mechanical behavior, and thermal management requirements.
Rigid Copper Busbars:
Fixed Connections with High Thermal Conduction Demand
Typical applications include:
- Series connections between battery modules
- Main positive and negative outputs to contactors and fuses
- Power Distribution Units (PDUs)
- DC bus systems in motor inverters
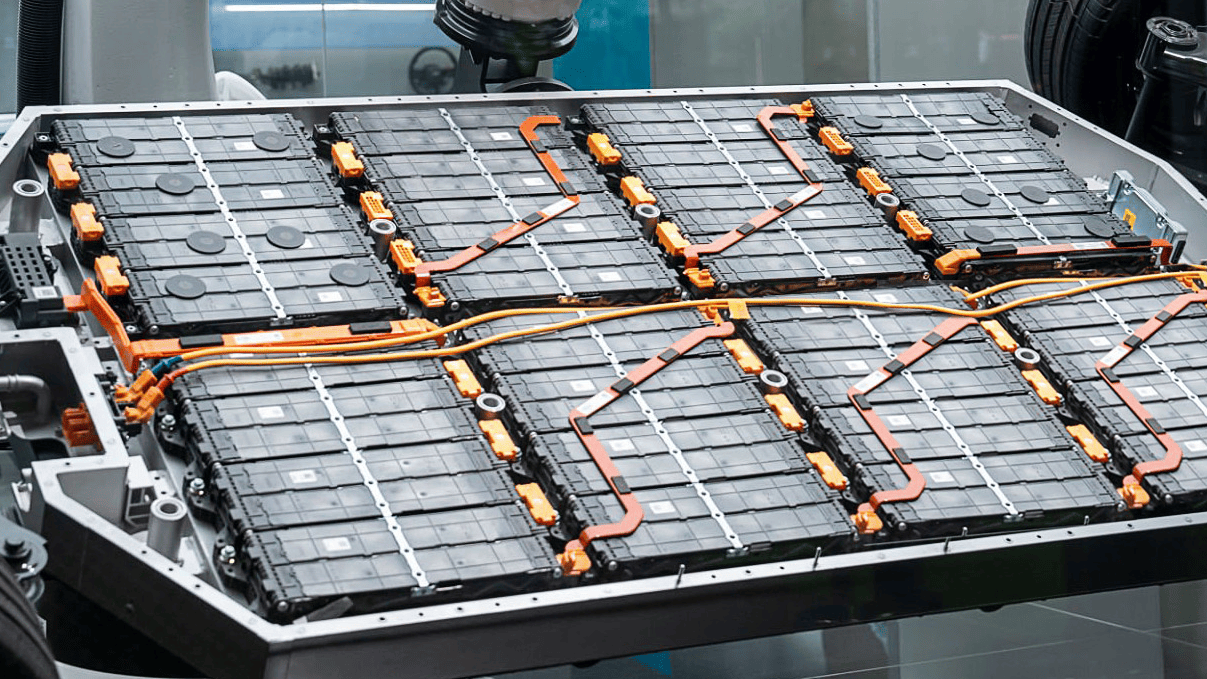
These locations feature fixed geometries, stable mounting interfaces, and close proximity to cooling systems. Rigid copper busbars provide ultra-low loop resistance and inductance while simultaneously acting as critical thermal bridges. They efficiently conduct heat generated under high-current operation into housings or liquid cooling systems, ensuring stable, low-temperature operation of key power components.
Flexible Copper Laminated Connectors:
Connections Requiring Compliance and Displacement Compensation
Commonly applied in:
- Interconnections between prismatic or cylindrical cells within battery modules
- Vibration-isolated connections between battery packs and BMS or high-voltage junction boxes
- Busbar interfaces affected by thermal expansion and contraction
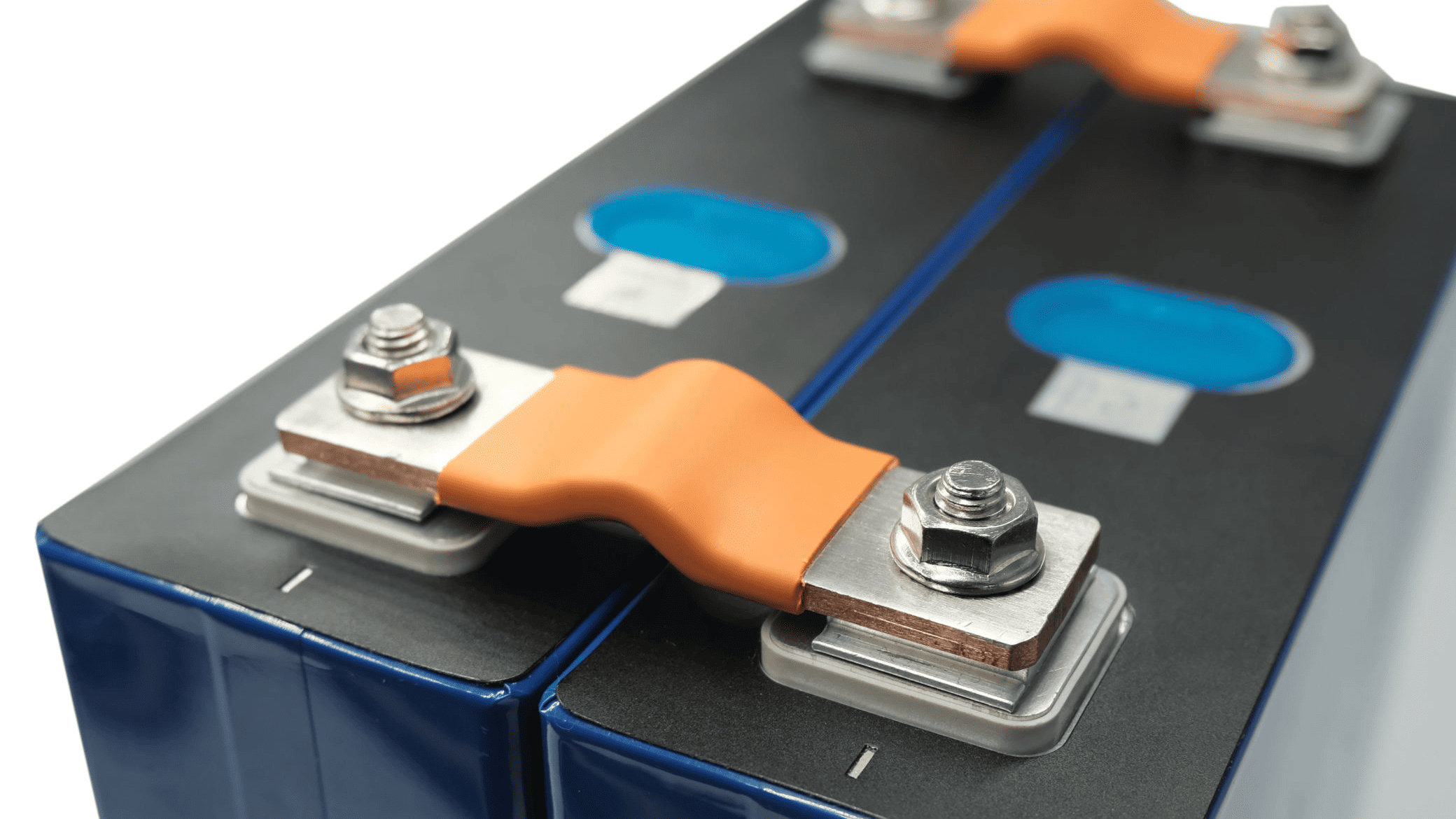
Their flexibility effectively compensates for manufacturing tolerances, cell swelling during charge/discharge cycles, and mechanical vibration under vehicle operating conditions. This prevents stress concentration at electrical joints and significantly enhances long-term reliability. In battery modules without dedicated forced cooling, the inherent heat dissipation capability of laminated connectors serves as a valuable supplementary thermal management mechanism.
3. Manufacturing Excellence: Precision Design and Integration
Selecting rigid copper busbars or flexible copper connectors is not a binary decision, but rather a system-level optimization within an integrated electrical–mechanical–thermal design framework. True engineering capability is reflected in three core dimensions:
3.1 Accurate Simulation-Driven Selection
Through advanced thermal and electrical simulations, temperature rise under multiple operating conditions is precisely evaluated. This enables:
Single-solution optimization (directional heat conduction or self-dissipation)
Hybrid rigid–flexible configurations tailored to specific system architectures
3.2 Advanced Manufacturing Processes to Ensure Performance
Rigid copper busbars: Manufactured using high-conductivity copper, combined with precision stamping, CNC machining, and nickel or tin surface plating to ensure low contact resistance and high-quality thermal interfaces. Integrated cooling channels or fin structures can be customized to support active thermal management designs.
Flexible copper laminated connectors: Produced using diffusion bonding under high temperature and pressure, achieving true metallurgical bonding between foil layers. This process effectively eliminates interlayer contact resistance and thermal resistance, delivering electrical and thermal performance comparable to solid copper—far superior to traditional bolted or partially brazed solutions. Copper–aluminum transition terminals and custom-shaped thermal end structures can be integrated as required.
3.3 System-Level Integrated Solutions
RHI is not merely a busbar component supplier, but a collaborative partner in new energy system thermal management design. Our portfolio includes rigid copper busbars for fixed mounting and directional heat conduction, flexible laminated connectors for displacement compensation, and rigid–flex composite busbars for transitional interfaces. Based on the customer’s system architecture, cooling strategy, and spatial constraints, RHI delivers optimized electrical interconnection and thermal management layouts tailored to each application.
Conclusion
In high-efficiency energy conversion systems, thermal control is a defining factor in electrical interconnection performance. Rigid copper busbars provide efficient, directional heat conduction, while flexible copper laminated connectors offer inherent heat dissipation and mechanical compliance. Leveraging deep expertise in thermal mechanisms and advanced manufacturing processes, RHI precisely matches single or combined solutions to customer requirements—ensuring effective heat control, high reliability, and long-term system performance.
With professional simulation capabilities, advanced manufacturing technologies, and a system-oriented design philosophy, RHI delivers low-temperature-rise, high-reliability electrical interconnection solutions for next-generation new energy products.
RHI ELECTRIC | Battery Interconnection Solutions