Battery Selection and Busbar Connections for EVs
EV Lithium Battery Selection and Busbar Connection Solutions
In new energy vehicles, the traction battery plays a role equivalent to the fuel tank in traditional ICE vehicles—it is the primary energy source and the core storage unit of the entire powertrain. A complete battery system is built from multiple subsystems including cells, modules, the Battery Management System (BMS), thermal management, high- and low-voltage wiring, insulation and structural components, as well as a protective enclosure. Together, they enable energy storage, power output and system-level safety.
As the “energy reservoir” of the vehicle, the battery system’s technical route directly shapes performance boundaries and vehicle positioning. Today, the market has clearly converged on two dominant chemistries: NCM/NCA and LFP.

1. Overview of Battery Types: Classified by Cathode Material
Current EV battery technologies are commonly categorized by their cathode material:
- NCM/NCA Lithium-Ion Batteries
- LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) Batteries
- LMO (Lithium Manganese Oxide)
- LCO (Lithium Cobalt Oxide)
- Ni-MH (Nickel-Metal Hydride) – mainly used in hybrid vehicles rather than pure EVs
Among these, NCM/NCA and LFP have become the global mainstream, serving distinct segments such as long-range passenger cars and cost-optimized or commercial EV platforms.
2. Why NCM and LFP Became the Two Leading Technologies
Competition in EV batteries ultimately stems from cathode chemistry.
NCM/NCA batteries are named after their nickel, cobalt, and manganese (or aluminum)-based cathodes, while LFP batteries utilize lithium iron phosphate.
They have become dominant because each chemistry delivers attributes that align well with specific application demands:
- NCM/NCA: High nickel content enables very high energy density, which directly translates into longer driving range—an essential factor for consumer EV adoption.
- LFP: Its strong P–O covalent bonds provide excellent thermal stability, long cycle life, and the advantage of eliminating cobalt, enabling a safer and more cost-effective solution.
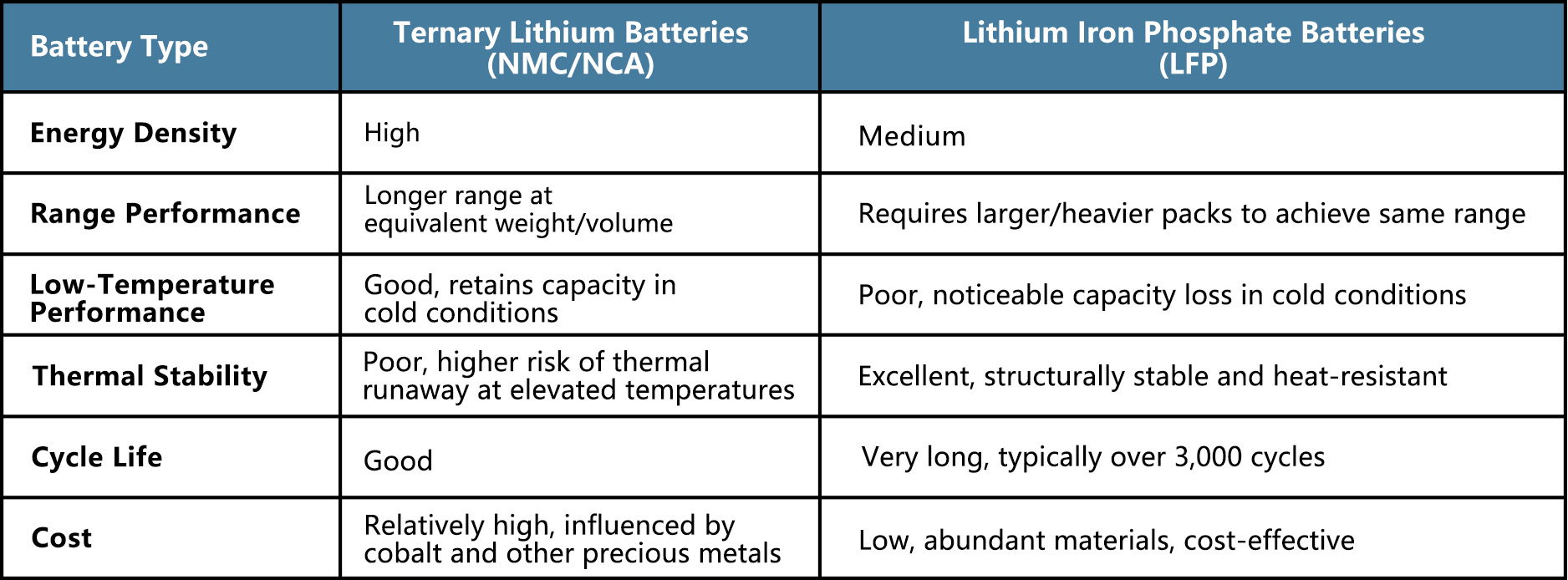
3. Deep Dive Into the Two Mainstream Battery Types
1) NCM/NCA Lithium-Ion Batteries
Advantages
- Excellent low-temperature performance
- High energy density for extended driving range
- High charge/discharge efficiency
Limitations
- Weaker high-temperature stability
- Higher material cost
- Requires more stringent thermal management for safety
NCM/NCA chemistries are widely adopted in mid-to-high-end EVs focused on long-range capability.
2) LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) Batteries
Advantages
- Outstanding high-temperature stability and low thermal runaway risk
- Lower overall cost
- Long cycle life, suitable for frequent charge/discharge use cases
Limitations
- Lower energy density and larger system volume
- Moderate low-temperature performance with noticeable range reduction in winter
LFP offers higher safety and better cost-effectiveness, making it a mainstream choice for commercial EVs and entry-level passenger vehicles.
4. Engineering Logic Behind Battery Selection
Battery chemistry is chosen based on the intended vehicle segment, operating conditions, and cost-performance balance:
- Long-range passenger cars → NCM/NCA
- Commercial vehicles, taxis, and utility models → LFP
- Cold-climate regions → NCM/NCA or enhanced thermal-managed LFP solutions
Key decision factors include energy density, safety, cost, cycle life, thermal behavior, and environmental adaptability.
Technologies like LCO and LMO are now marginal in EV power applications due to their inherent performance limitations. Ni-MH remains relevant mainly for hybrids.
5. Battery Architecture & Busbars: The Role of Critical Connection Components
Inside a battery pack, electrical and signal interconnections exist at three functional levels:
Signal-Level Connections (BMS sensing)
Used for voltage and temperature acquisition on each cell—essentially the “nervous system” of the battery.
Energy-Level Connections (Within modules)
Flexible connections between cells designed to accommodate mechanical expansion and contraction during charge/discharge.
Power-Level Connections (High-voltage inside the pack)
Responsible for high-current transfer between modules and the main positive/negative terminals. These require very high insulation integrity and mechanical robustness.
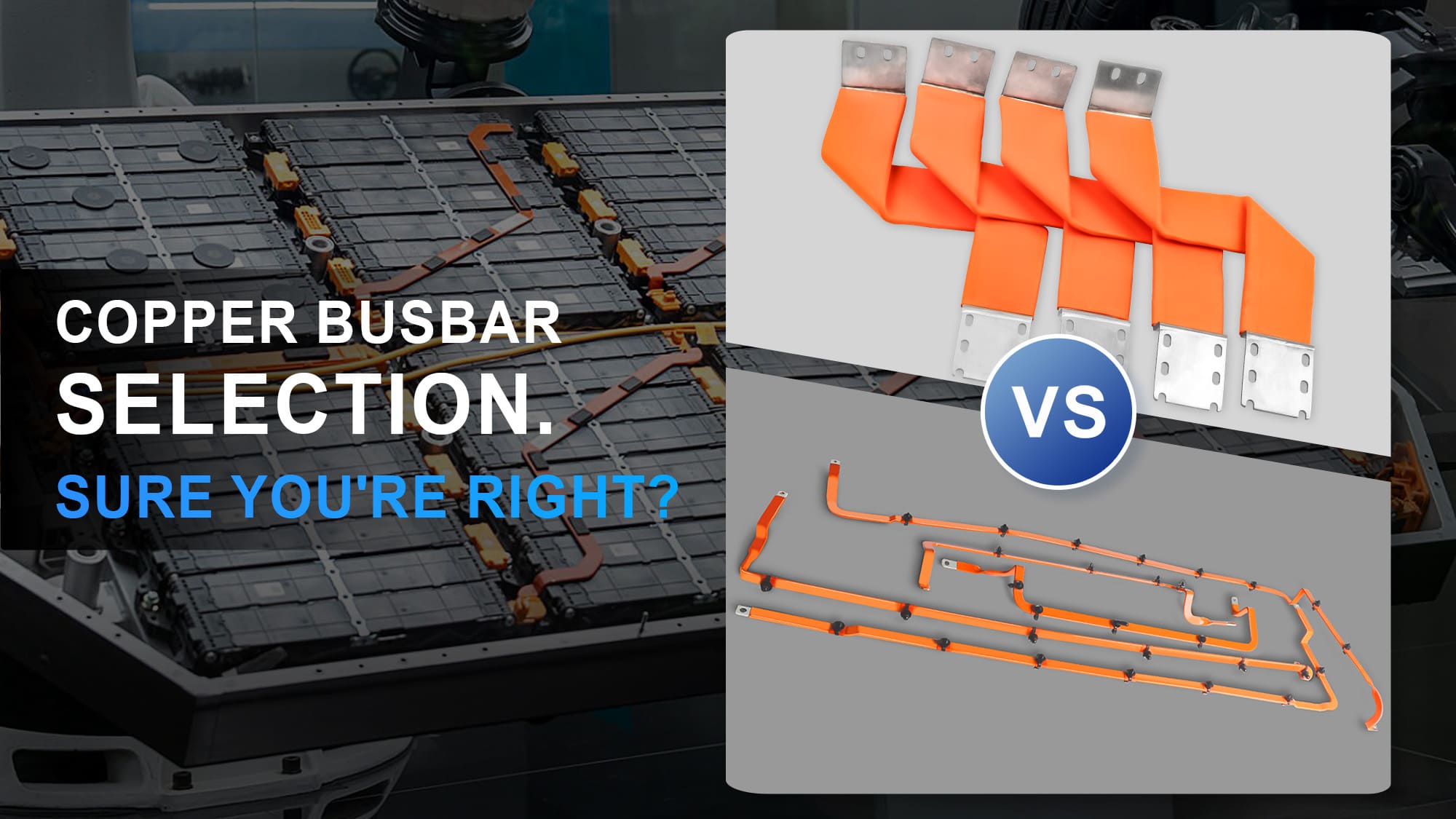
Every module and every HV node depends on safe, stable, low-resistance current pathways—this is where busbars play a decisive role.
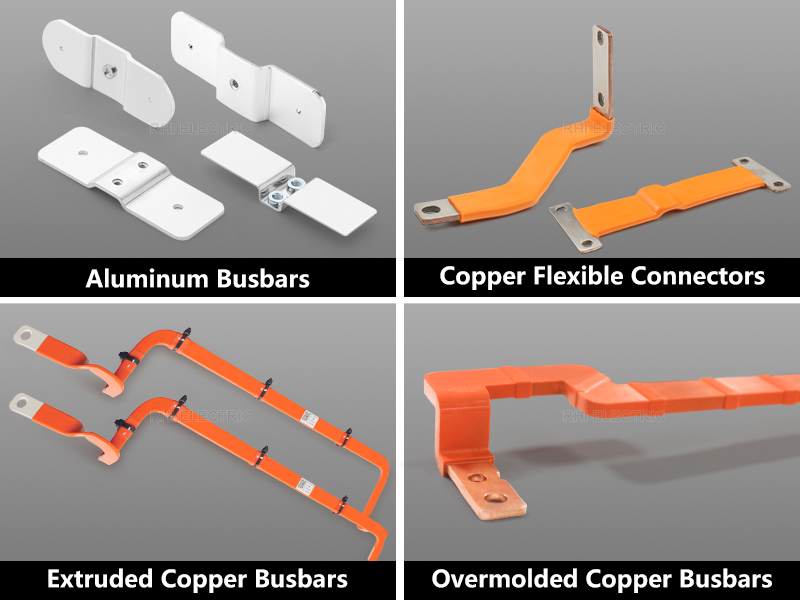
RHI provides engineered busbar solutions tailored to different battery chemistries and system architectures:
1) Aluminum Busbars — For BMS and Low-Current Sampling
- Lightweight with suitable conductivity for signal circuits
- Excellent formability for integrated structural layouts
- Cost-effective, contributing to overall system optimization
2) Flexible Copper/Aluminum Connectors — For Module-to-Module Connections
- Absorb vibration and thermal expansion
- Low resistance with high current-carrying capability
- Ideal for high-frequency, high-C-rate operating conditions
3) Rigid Busbars — For HV Power Circuits (100–800 V Platforms)
Available with insulated technologies such as dip-coating, extrusion, injection overmolding, or heat-shrink insulation:
- High current capability
- Integrated insulation improves safety and durability
- 3D forming options support tight packaging spaces
- Outer insulation can be engineered for high temperature, dielectric strength, and mechanical reliability
These battery busbars form the main electrical backbone of the HV system, ensuring stable and safe operation under demanding conditions.
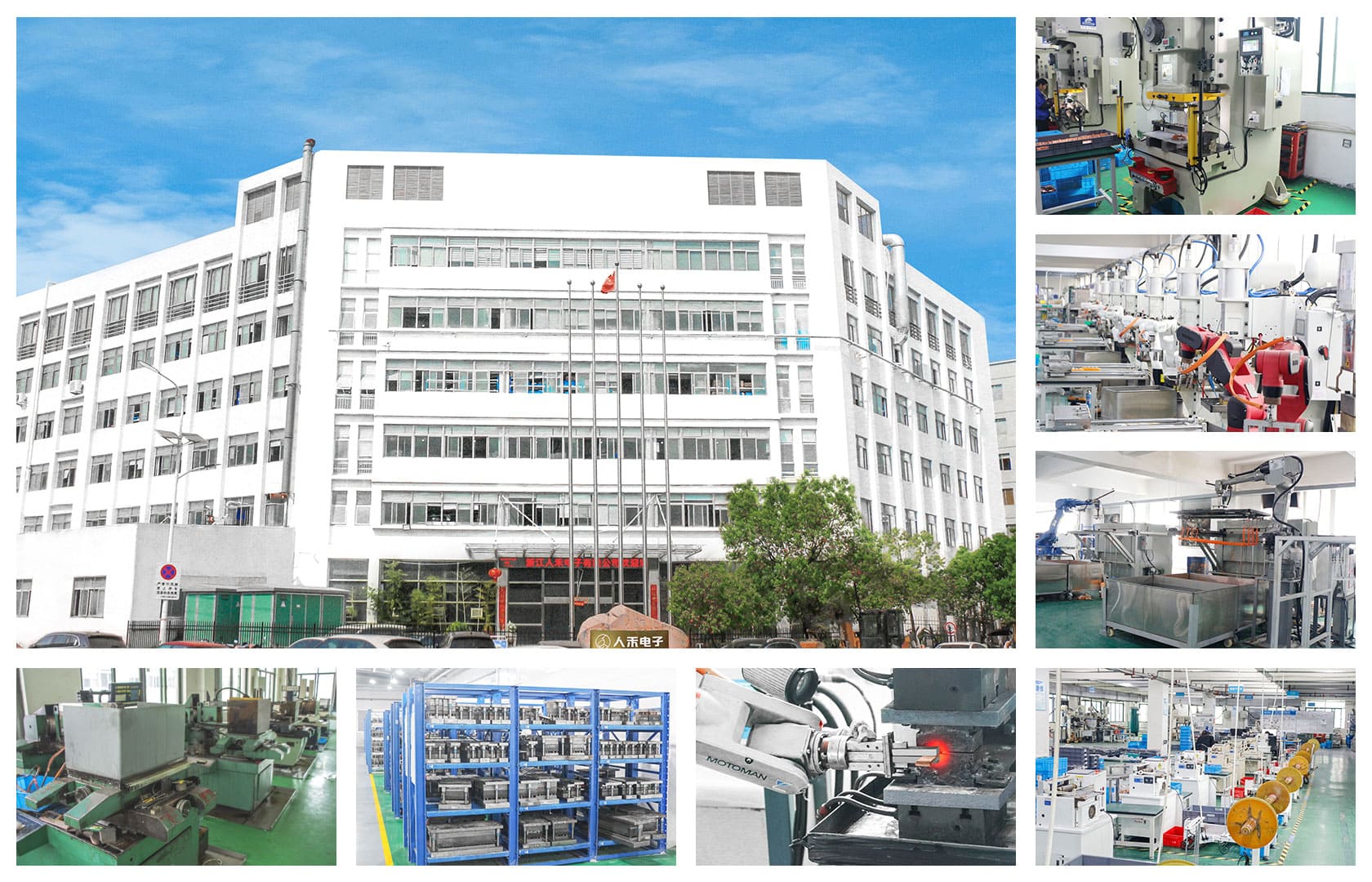
6. RHI: A Dedicated Supplier of EV Battery Connection Systems
With extensive experience in copper and aluminum busbar manufacturing and high-voltage interconnect design, RHI offers:
- Custom busbar design
- Material selection support (copper vs. aluminum)
- Electrical and thermal safety optimization
- High-reliability insulation processes
- Structural integration and lightweight engineering
RHI delivers optimized busbar solutions across NCM, NCA, and LFP platforms, enhancing safety, performance, and cost competitiveness for global EV manufacturers.