What Is a Bus Bar in Electrical Engineering? Full Guide and Applications
Discover what a bus bar is in electrical systems, how it works, the different types, materials used, key benefits, and where it’s applied. Cover everything you need to know about bus bars in modern power distribution.
Introduction
In modern electrical engineering, efficient and safe power distribution is a priority. Whether in commercial, industrial, or residential installations, the infrastructure that supports the flow of electrical energy must be both robust and reliable. One of the essential components facilitating this distribution is the bus bar. So, what is a bus bar in electrical systems, and why is it so important?
This blog aims to answer that question in-depth. We’ll explore the function, types, materials, advantages, applications, and design considerations of bus bars. Whether you're a student, an electrical engineer, or someone curious about how electricity is safely managed and distributed, this guide will provide valuable insights.
What Is a Bus Bar in Electrical Systems?
A bus bar (also spelled busbar) is a metallic strip or bar used in electrical power distribution to conduct electricity within a switchboard, distribution board, substation, or other electrical apparatus. Its primary role is to carry large current loads and connect multiple circuits together.
Think of a bus bar as the main highway for electrical current—allowing it to flow between components with minimal resistance and voltage drop. It replaces traditional wiring for high current applications and provides a cleaner, more organized alternative.

The Function of a Bus Bar
To truly understand what is a bus bar in electrical terms, we must consider its core functionalities:
1.Conducting Electricity Efficiently
Bus bars offer low impedance paths for current to travel across different electrical components.
2.Simplifying Power Distribution
Instead of having dozens of wires connecting each element, bus bars centralize power connections.
3.Increasing System Safety
By reducing clutter and organizing power flow, bus bars reduce the risk of overheating, short circuits, and electrical faults.
4.Allowing for Scalability
Electrical panels and power systems can be expanded easily by adding more branches to a bus bar.
Types of Bus Bars
Depending on the application and physical configuration, there are several common types of bus bars:
1. Single Bus Bar System
- Structure: One main bus bar.
- Use Case: Simple and cost-effective systems where continuity isn’t a high concern.
- Downside: Entire system needs to shut down during maintenance.
2. Double Bus Bar System
- Structure: Two parallel bus bars.
- Use Case: Applications requiring flexibility and uninterrupted service.
- Benefit: Loads can be transferred between bus bars without shutdown.
3. Main and Transfer Bus Bar System
- Includes a main bus and a backup (transfer) bar to switch circuits during maintenance or faults.
4. Ring Bus System
- Circuit breakers and loads are arranged in a ring configuration.
- Suitable for substations that need reliability and flexibility.
5. Mesh Bus System
- Often used in complex substations.
- Allows multiple connections and high redundancy.
Materials Used in Bus Bars
Understanding what is a bus bar in electrical systems includes knowing what they’re made of. The material affects performance, cost, and conductivity.
1. Copper Bus Bars
Advantages: Excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance.
Applications: Used in critical systems where performance is paramount.
Downside: Expensive and heavy.
2. Aluminum Bus Bars
Advantages: Lightweight and cost-effective.
Applications: Used in residential and light commercial installations.
Downside: Slightly lower conductivity than copper and more prone to oxidation.
3. Tin or Silver Plated Bus Bars
Advantages: Enhanced corrosion resistance.
Use Case: Humid or corrosive environments.
Design Considerations
Designing a bus bar system involves several critical considerations:
1. Current Carrying Capacity
Defined by cross-sectional area, material, and operating temperature.
2. Thermal Expansion
Especially in high-power systems, designers must account for material expansion and contraction.
3. Short-Circuit Withstand Rating
The ability of the bus bar to handle fault currents without damage.
4. Insulation and Spacing
Depending on the voltage, bus bars may require insulation or spacing to prevent arcing.
5. Mechanical Strength
Especially important in industrial environments where vibration or physical stress may be present.
Common Shapes and Configurations
Bus bars come in different shapes and sizes, based on the application:
- Flat Bars: Most common, offering high surface area and easy mounting.
- Round Bars: Sometimes used in compact spaces.
- Tubular Bus Bars: Used where cooling is a concern, or when mechanical strength is required.
They can also be layered or laminated to reduce skin effect at high frequencies (useful in AC applications).
Applications of Bus Bars
1. Electrical Panels
Central to every distribution panel and switchgear.
2. Power Stations
Facilitate the transfer of energy from generators to transformers.
3. Renewable Energy Systems
Used in solar and wind power systems to distribute DC or AC power efficiently.
4. Data Centers
Help manage complex power distribution needs with scalability.
5. Industrial Facilities
Enable power distribution across heavy machinery and automation systems.
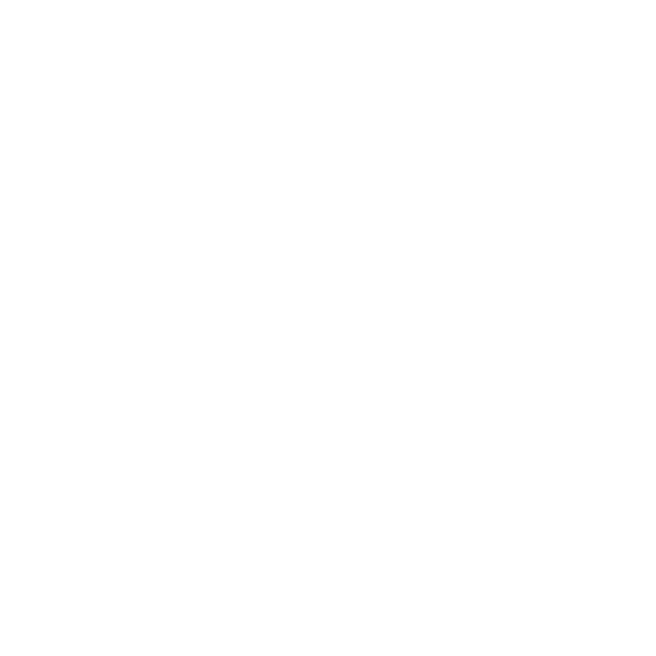
6. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
Modern EVs use bus bars to connect battery packs and manage high-current transfers.
Safety and Maintenance Tips
Use Insulated Bus Bars: Especially important in high-voltage environments.
Check for Loose Connections: Regular inspections reduce the risk of arcing.
Thermal Imaging: Helps detect overheating spots that may indicate faults.
Clear Labeling: All connections should be marked to simplify maintenance.
Keep Clean: Dust and moisture can cause tracking and corrosion.
FAQs
Q1: What is a bus bar in electrical panels?
A: A bus bar in electrical panels is a metal strip that distributes power to multiple circuit breakers or loads, replacing traditional wiring and improving organization and safety.
Q2: Why are copper bus bars preferred?
A: Copper has high conductivity, low resistance, and excellent thermal performance, making it ideal for high-performance and safety-critical applications.
Q3: Can bus bars be used in home installations?
A: Yes, though more common in commercial and industrial settings, compact bus bars are used in residential switchboards to manage power distribution efficiently.
Q4: How do bus bars handle high currents?
A: Their large cross-sectional area and solid material construction allow them to carry high current with minimal resistance and heating, making them suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Q5: Are bus bars safe?
A: Yes—when properly installed and maintained. Insulation, spacing, and protective housings help prevent accidents and ensure long-term safety.
Conclusion
So, what is a bus bar in electrical systems? It's a foundational component for efficient, safe, and scalable power distribution. From massive substations to the latest electric vehicles and compact data centers, bus bars play a crucial role in modern energy systems.
Their ability to simplify wiring, improve current distribution, and enhance safety makes them indispensable in today's increasingly electrified world. With continued advancements in materials, smart features, and sustainability, bus bars will remain a key player in the future of electrical engineering.